Partition circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc., and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape.
Represent and interpret unit fractions in the form 1/n as the quantity formed by one part when a whole is partitioned into n equal parts.
Represent and interpret fractions, including fractions greater than one, in the form of m/n as the result of adding the unit fraction 1/n to itself m times.
Read and write fractions, including fractions greater than one, using standard form, numeral-word form and word form.
Plot, order and compare fractional numbers with the same numerator or the same denominator.
Identify equivalent fractions and explain why they are equivalent.
Partitioning is the concept of "equal sharing," or splitting a shape or group of objects into equally-sized groups.
These shapes do not represent halves, thirds, or fourths, because they are not partitioned equally. Students can think about these as being "unfair" divisions of an object.
THese objects are partitioned equally. It's important for students to understand that each section represents an equal fraction of the whole, as labeled above.
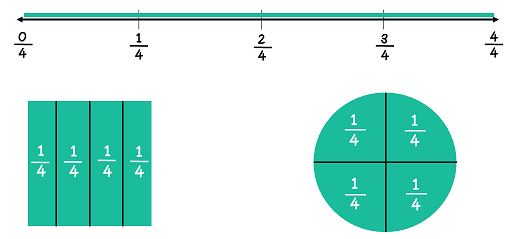
Fractions can be represented on a number line through shading, as shown. 4/4 (four-fourths) is the fraction represented on this number line.
Fractions can also be represented on a number line by plotting a single dot. 6/8 is plotted on this number line.
Students should be able to recognize fractions that are represented in different ways, like this fraction (3/4) represented on a number line and a circle diagram.